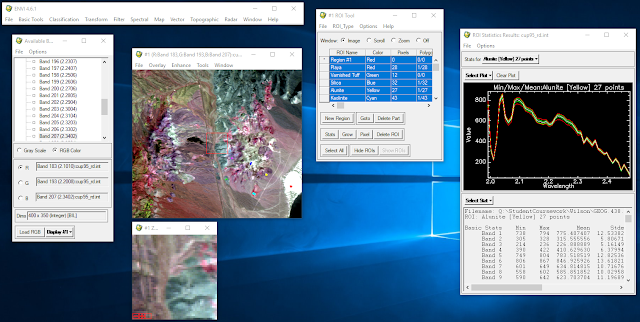
Goals and Background: In this lab hyperspectral data was introduced. The goal of the lab was to become familiar with various functions and procedures associated with this type of data. Hyperspectral data was atmospherically corrected using the FLAASH radiative transfer code method, hyperspectral signatures were plotted and compared to sample signatures, hyperspectral data was animated to show all bands, hyperspectral data was used in combination with various indecies to produce vegetation analysis data, and hyperspectral data was corrected for noise. Methods: Part 1 Section 1: Plotting hyperspectral signatures An JPL-calibrated AVIRIS image including 50 bands from 1.99 to 2.48 µm was brought into ENVI, and provided regions of interest of different minerals were opened after displaying the 183, 193, and 207 bands in RGB. Histograms for these ROIs were then opened and compared, paying special attention to features of the plots that could be used to identify one mineral from ...